Global Brand Strategy is the compass that guides how a company speaks to diverse audiences while staying true to its core promise. In today’s multicultural markets, brands win by aligning a clear strategy with local realities and expectations across channels. A well-crafted framework balances a strong global brand positioning with flexible adaptations that respect language, color symbolism, and cultural cues. From purpose and positioning to creative execution, the framework emphasizes scalable systems, regional insights, and disciplined governance that keeps messages coherent yet relevant. By measuring trust, familiarity, and resonance across regions, a brand can build loyalty without sacrificing its distinctive identity.
From a strategic vantage, brands think beyond borders by using an international branding lens that respects local taste, language, and tradition. Practitioners describe this as a cross-border approach where messaging and products are adapted to fit regional expectations without losing the overarching identity. Instead of a one-size-fits-all model, this mindset embraces local nuance, regulatory realities, and channel preferences to create consistent yet flexible touchpoints. In practice, teams build a unified framework that guides adaptation decisions, content creation, and experience design across markets. The result is a global footprint that still feels native to each audience, fostering trust and long-term loyalty.
Global Brand Strategy in Multicultural Markets: Aligning Global Brand Positioning with Local Realities
Global Brand Strategy in multicultural markets begins with a shared north star and a flexible system that respects regional identities. A well-crafted Global Brand Strategy blends high-level positioning with adaptable design and messaging so the brand remains globally recognizable while speaking locally. This means the global brand positioning communicates universal benefits—such as quality, reliability, or inspiration—while regional teams tailor language, channels, and cultural cues to fit their audiences. The result is a coherent, data-informed strategy that supports global branding goals across diverse markets without losing brand essence.
To implement effectively, establish localization playbooks, region-specific value propositions, and governance that protects core identity while enabling local agility. Build a hub-and-spoke brand architecture where the hub preserves the core values and spokes adapt copy, imagery, and packaging for local contexts. Invest in linguistic expertise, regional testing, and analytics to measure familiarity, resonance, and purchase intent by market, ensuring the strategy scales with quality and cultural sensitivity.
Cross-Cultural Marketing through Brand Localization: Winning in Multicultural Markets with Global Branding
Cross-Cultural Marketing in practice hinges on brand localization—translating language, symbols, and storytelling into culturally fluent experiences for multicultural markets. Brands should maintain a consistent voice and core values while adjusting tone, humor, imagery, and packaging to resonate with regional audiences. This convergence of cross-cultural marketing and brand localization ensures that global branding efforts feel native rather than foreign, guided by regional personas, local idioms, and culturally meaningful references.
Practical steps include developing region-specific value propositions aligned with the global brand positioning, creating localization playbooks for copy, visuals, and packaging, and piloting campaigns with clear KPIs. Central governance with dedicated regional leads helps safeguard consistency while empowering teams to test variants and optimize channels. The result is a scalable approach that sustains a global brand identity across multicultural markets and deepens relevance through local partnerships and experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can a Global Brand Strategy balance standardization with localization in multicultural markets?
A well-crafted Global Brand Strategy aligns core brand purpose, positioning, and identity (the hub) while allowing regional adaptations (the spokes) to reflect local realities. To balance global branding and localization, establish a hub-and-spoke framework, define region-specific value propositions, create localization playbooks for copy and visuals, and implement approval gates to protect brand integrity. This approach preserves brand equity across cultures while staying relevant in multicultural markets.
What metrics and governance support a Global Brand Strategy in cross-cultural marketing across multicultural markets?
Implement a governance model with regional leads to balance global guidelines with local learnings. Track metrics that matter for global branding in cross-cultural marketing: brand health (familiarity, associations, preference) and business impact (share of voice, market penetration, regional revenue). Use localization governance and region-specific pilots to test and refine the global brand positioning across multicultural markets. Regular brand audits and knowledge sharing ensure the global brand positioning stays recognizable yet locally resonant, preserving consistency while enabling local adaptation.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Global brands compete across borders in a multicultural marketplace; success hinges on a Global Brand Strategy that respects cultural nuance while preserving core brand essence. Aim to align global objectives with local realities to speak to diverse audiences without losing identity; the goal is to harmonize, not homogenize, creating a brand that is globally recognizable and locally resonant. |
| Understanding the multicultural market environment | Different regions bring distinct preferences, rituals, and channels. A Global Brand Strategy must account for language, color symbolism, media habits, and purchaser intent; gather regional insights, test messages, and design flexible brand systems; establish a unifying narrative while allowing regional adaptation; grounded in data and guided by consistent brand values with cultural sensitivity. |
| Core elements of a Global Brand Strategy | Pillars: (1) clear brand purpose, resonant across cultures; (2) strong brand positioning with room for localization; (3) cohesive brand voice and visual identity that is recognizable yet adaptable; (4) scalable brand architecture; translate into a global messaging framework, flexible creative brief, and brand standards that regional teams can implement with minimal friction. |
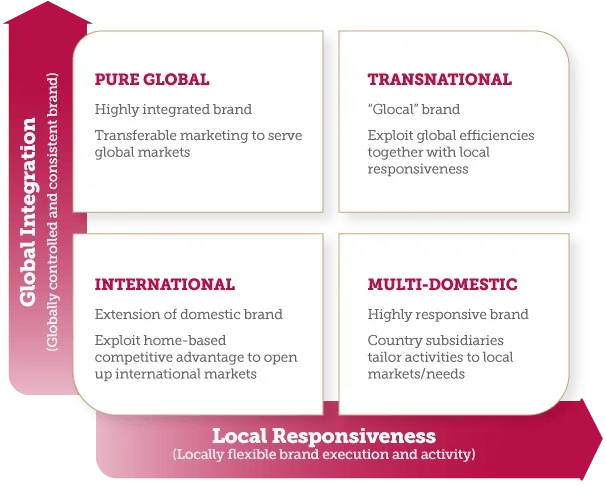
| Localization vs Standardization | Standardization yields efficiency and strong global recognition but can feel alien if local culture is ignored. Localization boosts relevance but can dilute if overdone. Use a hub-and-spoke model: a central, globally grounded brand system (hub) with regional adaptations (spokes) that maintain core values. Steps: region-specific value propositions aligned with global positioning, localization playbooks for copy/imagery/packaging, and approval gates to protect brand integrity while enabling local agility. |
| Global brand positioning in a multicultural context | Positioning must translate across cultures without losing its edge. A strong global position answers: what unique benefit does the brand provide across cultures? Regions tailor messaging for locally meaningful benefits; test against regional personas and adjust for language, humor, and symbols. Preserve a recognizable brand signature while enabling native-feeling local talk tracks. |
| Messaging, channels, and content strategy for multicultural audiences | Define core messages that travel well and translate locally. Content calendars balance evergreen brand stories with region-specific campaigns. Channel strategy varies by region (short-form mobile video vs. long-form/community-led content). Use data-backed audience segmentation to test and optimize variants that resonate with local language and cultural references. Create a narrative that feels universally recognizable yet locally meaningful. |
| Product, packaging, and experiential localization | Adapt product relevance and packaging aesthetics to local regulations and consumer expectations while preserving brand fidelity. Consider formulations, sizes, naming, visuals, color psychology, and symbols that differ by region. Prototyping and local testing, plus cross-functional collaboration, ensure the local experience aligns with the global story. Tailor in-store experiences, digital interfaces, and service touchpoints to be regionally respectful yet cohesive. |
| Measurement, optimization, and governance | Use metrics that reveal global performance and local effectiveness: brand health (familiarity, association, preference) and business metrics (share of voice, market penetration, regional revenue). Conduct regular audits to enforce standards while enabling localization. Maintain a central governance model with regional brand leads; feed local learnings back to the core team. Continuous learning through A/B tests, regional pilots, and cross-market knowledge sharing sustains relevance. |
| Case for action and implementation framework | Begin with a brand diagnostic to identify strengths and cultural opportunities in each market. Develop a global-to-local playbook defining the core system, localization guidelines, and approval processes. Build a regional cadence plan with priorities, budgets, and success metrics. Establish cross-functional workstreams and a routine for sharing best practices. Invest in capability development—linguistic expertise, cultural training, and data analytics—to empower teams to act quickly and adaptively. |
| Conclusion (summary) | Conclusion: Global Brand Strategy is not about erasing cultural differences; it is about discovering the shared human values that connect audiences across borders. By balancing standardization with localization, aligning global positioning with regional realities, and continuously measuring impact, brands can win in multicultural markets without compromising integrity. When brand teams work together across regions, the result is a cohesive, adaptable strategy that drives growth, trust, and lasting loyalty in a diverse world. |
Summary
Conclusion not displayed in the table; see below for a descriptive closing paragraph.