The Global Net-Zero Mission has shifted from a lofty ambition to a practical framework that informs how modern businesses operate, innovate, and invest, guiding strategy across products, markets, governance, and talent development in an era defined by climate risk, capital markets, and public accountability. As climate science tightens and investor expectations rise, leaders turn to net-zero roadmaps for businesses to translate ambition into concrete actions, embedding measurable milestones, governance oversight, and transparent disclosures that earn trust from customers and capital alike. Effective strategy tools hinge on corporate sustainability strategies, clear accountability, and empowered cross-functional teams, ensuring decarbonization efforts align with growth, resilience, and long-term value creation across operations, finance, and supplier ecosystems. A disciplined approach highlights decarbonization in business while balancing investment in energy efficiency, electrification, and low-carbon inputs with a robust plan for supply chain decarbonization, all supported by credible roadmaps. Measuring progress, aligning incentives, and fostering partnerships with suppliers, customers, and regulators ensures the journey translates ambition into measurable outcomes, sustaining momentum and delivering resilience, competitive advantage, and social value in a low-carbon economy.
From a broader perspective, the push toward climate-neutral operations is reshaping corporate planning, risk management, and value creation across industries. This global transition uses a low-carbon transformation playbook that emphasizes governance, capital allocation, and partnerships to unlock practical decarbonization actions. Rather than isolated projects, firms are designing integrated strategies that align product development, sourcing, and operations with measurable environmental and financial outcomes. By examining energy use, supplier networks, and lifecycle impacts through an ESG lens, organizations can anticipate policy shifts, manage risk, and access capital for sustainable growth.
Global Net-Zero Mission in Practice: Aligning Governance, Strategy, and Emissions Reduction Targets
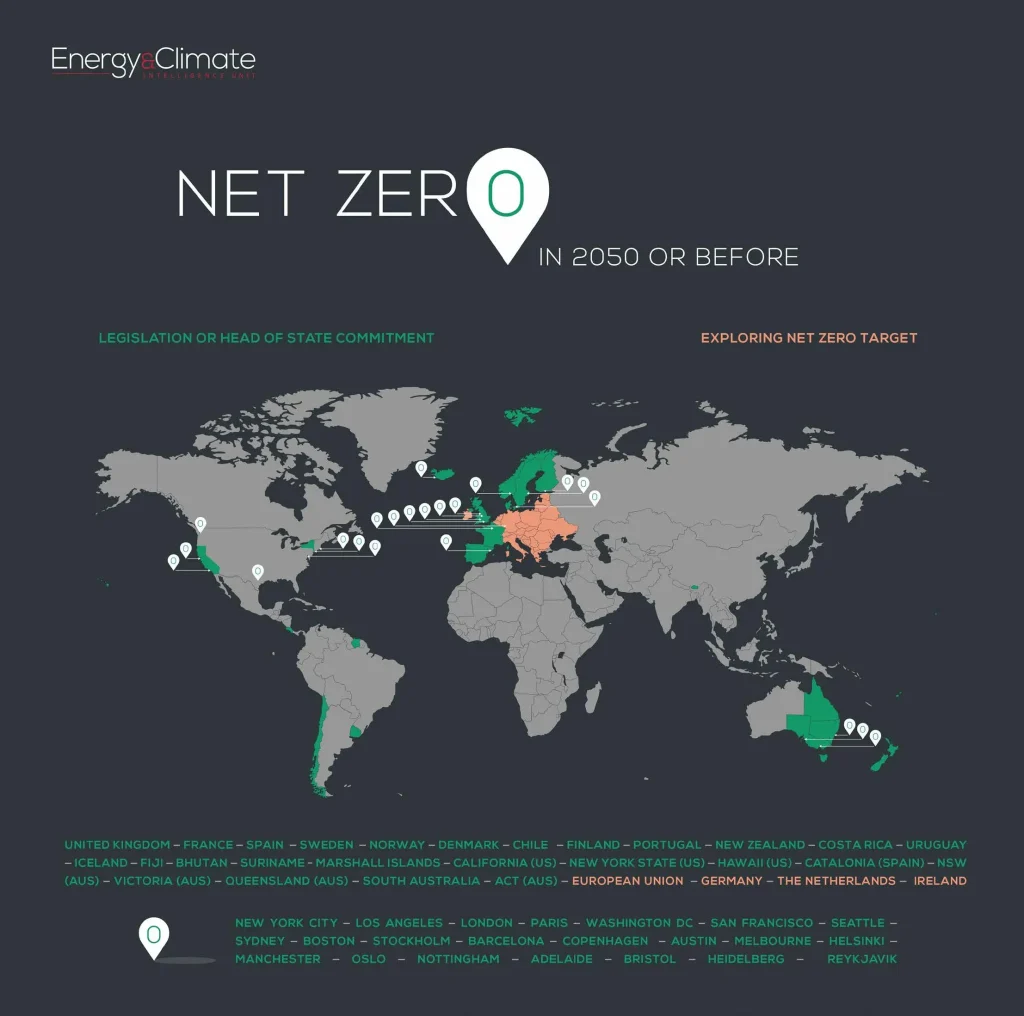
The Global Net-Zero Mission has evolved from a distant aspiration to a practical framework that guides every corporate decision. As climate science tightens and investor expectations rise, organizations are pressed to align operations with a net-zero pathway while preserving growth and competitiveness. This shift makes corporate sustainability strategies integral to business planning, with emissions reduction targets acting as anchors for strategy, investment, and risk management.
In practice, embracing the Global Net-Zero Mission means more than pledges—it requires clear governance and disciplined execution. Boards should demand transparent carbon metrics, and executives must weave decarbonization into strategic planning. Cross-functional teams spanning R&D, operations, procurement, and finance coordinate net-zero roadmaps for businesses, ensuring accountability, financing alignment, and credible progress across all activities including supply chain decarbonization.
The broader impact includes resilience benefits: a robust decarbonization program can dampen exposure to energy price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and reputational risks. By integrating decarbonization into core strategy and product design, companies strengthen competitive advantage while contributing to society-wide climate goals.
Global Net-Zero Mission: Driving Corporate Sustainability, Roadmaps, and Accountability
A practical path under the Global Net-Zero Mission centers on translating ambitious goals into a coherent plan—our net-zero roadmaps for businesses. These roadmaps translate long-term objectives into a sequence of actions with defined owners, milestones, and financial plans, providing clarity for governance, budgeting, and performance tracking.
Key components include a rigorous baseline emissions assessment across Scopes 1, 2, and 3, setting emissions targets aligned with frameworks like the Science Based Targets initiative, and identifying decarbonization levers such as energy efficiency, electrification, renewable energy procurement, and sustainable materials. The roadmap also emphasizes supply chain decarbonization and the integration of climate considerations into financial decisions, ensuring that governance and accountability reinforce steady progress.
The Role of Measurement and Collaboration in Net-Zero Progress
Measurement and disclosure underpin credibility in the Global Net-Zero Mission. By tracking progress against milestones and reporting transparently, organizations build trust with investors, customers, and employees. Regular measurement of emissions across Scopes 1–3, supported by external audits and standardized ESG metrics, helps ensure that decarbonization efforts translate into real, verifiable outcomes.
No single company can achieve net-zero alone. The mission thrives through policy support, green finance, and cross-industry collaboration. Partnerships with suppliers, customers, and regulators accelerate decarbonization in business models and value chains, enabling scalable supply chain decarbonization and shared innovations in technology and process improvements.
Net-Zero Roadmaps for Businesses: Structure, Investment, and Accountability
Net-zero roadmaps for businesses provide a practical framework to translate aspirational carbon goals into actionable programs. A credible roadmap outlines clear ownership, defined milestones, and linked financial plans, ensuring that decarbonization is embedded in governance and operations.
The roadmap structure typically includes baseline emissions assessment, targeted reductions, and a suite of decarbonization levers—ranging from energy efficiency and electrification to sustainable procurement and on-site generation. Financial integration ensures climate risk is reflected in capital allocation, while governance mechanisms and performance metrics keep teams accountable. In this way, net-zero roadmaps for businesses become a living tool for corporate sustainability strategies and day-to-day decision-making.
Strategic Pathways for Decarbonization: From Targets to Customer Value
Setting ambitious emissions reduction targets is only the first step. The Global Net-Zero Mission requires translating those targets into customer value through decarbonization in business models, products, and services. By focusing on energy efficiency, responsible sourcing, and low-carbon product design, companies can reduce lifecycle emissions while enhancing competitiveness and customer trust.
Supply chain decarbonization then becomes a strategic imperative, with collaborative supplier engagement, shared targets, and joint investment in low-carbon solutions. Such alignment strengthens resilience, reduces total cost of ownership, and supports a broader corporate sustainability strategy that resonates with investors and stakeholders who prioritize climate-aware governance and transparent emissions reporting.
Governance, Policy, and Ecosystem Collaboration in Net-Zero Strategy
A robust net-zero program requires governance structures that assign clear accountability and align incentives with long-term decarbonization outcomes. Board oversight, cross-functional steering committees, and climate-related disclosures ensure that emissions reduction targets are integrated into strategic planning and financial decisions.
Ecosystem collaboration—through policy engagement, public-private partnerships, and market-standard disclosures—helps scale net-zero initiatives. By participating in industry coalitions and adopting standardized reporting, companies can accelerate supply chain decarbonization, unlock green financing, and create a more predictable policy environment that supports sustainable growth.
Measuring Progress: Transparency, Verification, and Value Creation
Measuring progress is essential to sustaining momentum on the Global Net-Zero Mission. Companies should monitor Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, align with common accounting standards, and provide regular progress disclosures. Linking internal incentives to net-zero milestones strengthens discipline and accelerates emissions reduction targets achievement.
External verification, third-party audits, and assurance bolster credibility with investors, customers, and regulators. Transparent reporting of ESG metrics tied to strategic outcomes not only reduces reputational risk but also demonstrates a genuine commitment to decarbonization in business and long-term value creation.
Financial Implications: Capital Allocation and Climate-Driven ROI
Integrating climate risk and opportunity into capital allocation is a cornerstone of net-zero roadmaps for businesses. Climate-related financial disclosures, scenario analysis, and investment in low-carbon technologies align ROI with decarbonization goals, supporting sustainable growth and investor confidence.
Financial integration also encourages the deployment of renewable energy, energy efficiency upgrades, and supplier-transition programs. By treating decarbonization as a financial priority, firms can improve predictability of energy costs, reduce exposure to regulatory penalties, and attract capital from investors seeking resilient, sustainable portfolios.
The Path Forward: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Business Models
The Global Net-Zero Mission calls for resilient business models that excel in a low-carbon economy. Companies that embed decarbonization into product design, operations, and partnerships are better positioned to meet evolving customer expectations, withstand policy shifts, and capitalize on new green markets.
By prioritizing supply chain decarbonization, engaging suppliers in joint climate actions, and investing in scalable low-carbon technologies, organizations can accelerate progress toward net-zero while maintaining growth and competitiveness. This proactive approach turns climate leadership into a source of value, efficiency, and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Global Net-Zero Mission and how do net-zero roadmaps for businesses drive action?
The Global Net-Zero Mission is a practical framework that requires organizations to decarbonize while sustaining growth. Net-zero roadmaps for businesses translate this ambition into concrete actions with baseline emissions assessment, time-bound emissions reduction targets, clear ownership, and investment plans. They also emphasize decarbonization levers across operations, supply chain decarbonization, governance, measurement, and transparent disclosures to track progress and drive value.
How can organizations align corporate sustainability strategies with emissions reduction targets under the Global Net-Zero Mission?
To align corporate sustainability strategies with emissions reduction targets, leadership should embed decarbonization into business strategy, assign clear accountability, and integrate climate risk into capital allocation. This includes setting credible emissions reduction targets aligned with established frameworks, measuring progress across Scopes 1–3, and pursuing supply chain decarbonization through supplier engagement. Strong governance, cross-functional collaboration, and transparent reporting enable implementation of net-zero roadmaps for businesses while delivering resilience and long-term value.
| Theme | Key Points | Notes / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Why it matters | The climate crisis requires rapid emissions reductions. The Global Net-Zero Mission frames responsibility for decarbonization while continuing to innovate and serve customers. It involves setting ambitious targets, investing in low-carbon technologies, and designing products/services that enable customer transition. A robust plan also enhances resilience by reducing exposure to energy price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and reputational risk. | Examples: setting targets aligned with credible frameworks; investing in renewables and energy efficiency; designing products with lower lifecycle emissions. |
| Business role in the Global Net-Zero Mission | Businesses are key actors, not just CSR. Sustainability is a core strategic driver affecting cost of capital, talent, and market share. Leadership in governance, strategy, and execution is essential; cross-functional teams coordinate R&D, operations, procurement, and finance. | Examples: boards demanding carbon metrics; executives embedding decarbonization in strategic planning; cross-functional teams driving action. |
| Net-zero roadmaps: structure & components | A credible roadmap translates long-term goals into a sequence of actions with clear owners, milestones, and financial plans. |
|
| Industry perspectives and practical case studies | Roadmaps vary by sector but share a customer-centric approach that balances decarbonization with reliability and cost competitiveness. | Examples: manufacturing prioritizes energy efficiency and low-carbon inputs; tech emphasizes efficient data centers and software-enabled decarbonization; transport/logistics focuses on fleet electrification and route optimization. |
| Measuring progress: from targets to outcomes | Progress is measured across Scopes 1, 2, and 3 using common accounting standards, with regular reporting and external verification. | Notes: align internal incentives with net-zero targets to sustain momentum; use external audits to build credibility with investors and customers. |
| Policy, market, and collaboration dimension | Policy support, green financing, and industry collaboration help scale solutions. Public-private partnerships and standardized disclosures create a level playing field. | Notes: collaboration across industries accelerates diffusion of best practices and scale-up of new technologies. |
| Challenges and opportunities on the journey | The journey includes upfront costs and uncertain returns; supply chains can complicate decarbonization. Opportunities include stronger brand value, better risk management, sustainable finance access, and talent attraction/retention. | Strategy implication: integrating decarbonization into core business decisions can yield competitive advantage. |
Summary
Conclusion: the imperative to act now